Selection of the compressor on the main characteristics
Owners of private houses or garages often have situations when it is necessary to use pneumatic tools for various housework or for car maintenance. Since the pneumatic tool works only from compressed air, for its effective operation it is necessary to make the right choice of compressor.
Content
Purpose and scope of the compressor
The main purpose of the compressor is to produce compressed air that accumulates in the receiver and is fed into the pneumatic system.. Various equipment and pneumatic tools are connected to the latter.
The compressor is needed to perform the following operations:
- painting various surfaces, applying primer, paint or varnish;
- blowing off chips and dust of various parts in production or during repair work;
- applying corrosion preventing compounds to hard-to-reach places of the car;
- pneumatic polishing and grinding machines;
- operation of pneumatic vice and various clips;
- work screwdrivers and wrenches.

Characteristics for compressor selection
Getting to the choice of the compressor, you must have a clear idea for what purposes it will be used. Only with this information, you can pick up the unit, taking into account its main characteristics.
Operating pressure
The degree of compression that the compressor is able to create is a fundamental characteristic for this unit. It depends on the working pressure indicator whether a pneumatic tool will work with the required efficiency.
The pressure in the documentation for the compressor can indicated in the following units:
- Pascals (Pa);
- bars (bar);
- atmospheres (atm);
- millimeters of mercury (mm. Mercury.);
- kilogram-force per square meter see (kgf / cm2);
- in pounds per square. inch (psi).
The most commonly used units such as Pa and Bar (1 bar = 0.1 Pa).
Important! When choosing a device, you should take into account the loss of air pressure while it passes the path to the tool. The pressure may decrease due to the long duct, the presence of a multitude of kinks, flaps, valves, etc. Therefore, for normal operation of the instrument, you will need a compressor with a small margin of pressure.
For example, the device can squeeze air to a maximum of 10 Pa. But until he reaches the instrument along the line, the pressure drops to 6 Pa. If the tool can work effectively with this pressure, then this is good. But if the pneumatic equipment is designed for high rates of working pressure, then the compressor will have to be replaced with a more powerful one.
Performance
Under the capacity of the unit is usually meant the volume of compressed air, which it can produce per unit of time.Compressor capacity is measured in l / min or m3/ min and is not a stable indicator, because it depends on the model of the unit and the ambient temperature.
Power
Indicated in the passport to the unit in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (hp) (1 kW = 1.36 hp). In principle, the power of the unit determines its performance. Accordingly, the higher this indicator, the greater the power of the engine installed in the compressor. How to calculate the performance will be discussed further, therefore, it is not necessary to calculate the compressor power.
Operating voltage and frequency
Air compression equipment can operate from both a three-phase and single-phase network. Three-phase network is rare for private houses, therefore three phase units are professional and are usually intended for production. If the compressor will be connected to a 220 V household power supply, then in this case it is necessary to choose single phase unitcorresponding to the voltage and frequency in the network, which in Russia is 50 Hz and is the only standard.
Important! Take into account the starting current of the unit, which is quite large. On a “subsiding” network, the engine of the apparatus will start badly. It is necessary to connect the compressor to a separate outlet, connected to a cable with a sufficient cross-section.
Receiver volume
Receiver is cumulative capacityin which air is pumped from the compression chamber of the compressor. The number of switching on (off) the unit depends on the volume of the receiver. The greater the volume of the tank, the less will be included the apparatus for pumping air into it. But to fill a large receiver, the unit will take more time. Of course, the smaller receiver will fill up faster, but the pressure in it will fall just as quickly when the instrument is working.
Noise level
Compressor noise is a huge disadvantage. The compressor, especially of the piston type, produces a strong noise, sometimes reaching up to 85 dB, which can be compared with the noise near the railway.Therefore, choosing a unit, note Is the insulation installed on it?and what level of noise it emits. It is desirable that it does not exceed 68 dB. If these figures specified in the instructions to the device, you do not say anything, you can ask the seller to check the compressor for noise, turning it on.

Screw compressor GUDEPOL 7.5 kW 500L
Manufacturer
A large number of different companies are engaged in the production of compressor equipment, which is why the market for these products is in a crowded state. Therefore, the brand of the compressor should also be taken into account if you want to buy a good unit. Home and professional craftsmen are advised to select a compressor among products from famous brands, such as Metabo, Fini, Fubag and Abac.
Compressor Performance Calculation
The design of the compressor determines its performance.Piston and screw devices are most commonly used to compress air.
Performance piston unit
To calculate the performance of the compressor, you should consider the number of pneumatic tools that will be connected to it, as well as its nominal characteristics.
The calculation of performance is made according to the formula:
Q = ((Q1 * K1) / 0.65) + 30%, where:
- Q - the overall performance of the device;
- Q1 - air consumption of equipment connected to the duct;
- K1 - the utilization rate of the tool;
- 0.65 is an approximate indicator of the efficiency of the compression chamber, taking into account the pressure loss in the line;
- 30% - performance margin.
For example, the working air flow rate of a wrench (specified in the passport) is 400 l / min. Therefore, Q1 = 400.
Also when using this tool is inevitable pauses occurwhich occupy about 80% of the entire workflow. Hence, the utilization rate of the tool will be equal to 20%, that is, K1 = 0.2.

We substitute the known values into the formula: Q = ((400 x 0.2) / 0.65) + 30% = 160. It turns out that for normal operation of this wrench a compressor with a capacity of 160 l / min is required.
If you need to connect several tools to the air line, for example, a grinder and a drill, then the values of their air consumption are summed up (200 + 240) and substituted into the above formula. But in this case, you should consider synchronization factorwhich determines the performance of the compressor while using multiple tools. Usually for 2 points of compressed air consumption, the synchronicity factor is 0.95. Substituting the values into the formula, we get: Q = ((200 + 240) x 0.2) x 0.95 / 0.65 + 30% = 167.2 l / min. It is this amount of air per minute that the compressor will need to feed into the system to ensure the normal operation of the two pneumatic tools.
Screw compressor capacity
This value can be represented as the sum of the volumes limited by screws inside the compression block, which are fed to the exit from it per unit of time. Calculated performance by the formula: Qt = l * m1 * n1 * f1 + l * m2 * n2 * f2where:
- Qt - unit performance, theoretical;
- I is the length of the screw of the compression unit;
- m1 - indicator of the number of visits made by the lead screw;
- n1 - frequency with which the lead screw rotates, with-1;
- f1 - trough area on the lead screw, m2;
- m2 - indicator of the number of visits made by the driven screw;
- n2 - frequency with which the driven screw rotates, with-1;
- f2 - the area of the depression on the driven screw, m2.
If we consider that m1 * n1 = m2 * n2 = m * n, the formula can be simplified: Qt = l * m * n * (f1 + f2).
In reality, the actual flow rate is affected by various overflows inside the compressor unit and leakage through the seals, as well as various energy losses. Therefore, it is always less than theoretical consumption, and mathematically taken into account feed rate.

Based on the foregoing, the actual performance is determined by the formula Qd = Qt∙ηP - QPwhere:
- Qd - actual performance;
- QP - the amount of air leakage through the seals;
- ηP - feed rate.
Required parameters for various pneumatic tools
Choosing an air compressor, which ensures the operation of the tool, it is not always worthwhile to strive for large indicators of its performance and receiver size, since the average characteristics of the unit will be enough for normal operation of most pneumatic equipment. You can save on this, because overpaying for power and other parameters, the use of which is not foreseen in the future, is impractical.
Any pneumatic tool has a nominal pressure and air flow, at which it can effectively perform its functions. The table below shows comparative data for pneumatic tools, often used with air compressors.
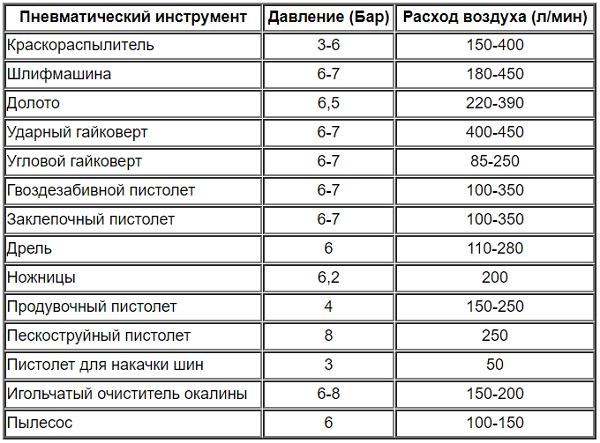
Using this table, you can easily pick up a pneumatic tool under the parameters of the compressor, or vice versa - the unit under the parameters of the tool. For example, it is possible to understand which pneumatic tool can work at a pressure of 7 bar, and for which a more powerful blower is required.
Tips for choosing the type of compressor for working in the garage
Among the many options for compressors, screw and piston units are considered the most common. Screw machines are expensive installations that are more suitable. for large auto repair shops with a high level of air consumption. Thanks to the use of a screw compressor, several points of consumption of compressed air can be made at once, for example, for the projection tool, a device for tire inflation, a tire mounting station, etc.
For medium or small car service, as well as for the garage is better to buy a piston compressor. Piston-type units are the most popular due to reasonable prices for them, ease of use and reliability. With small dimensions of this equipment it is possible to connect several independent air ducts to it. Reciprocating compressors are of two types.
- Direct drivewhen the engine shaft is located on the same axis as the crankshaft of the compression block. Direct-drive devices (coaxial) are often used in the garage and in field work. But you should know that this type of compressor has a limited resource, about 6000 hours.
- Belt driven: the shafts of the block and the engine have pulleys and are interconnected by means of a belt drive. The service life of a belt-driven compressor is much longer, since the pulleys on the engine shaft and on the crankshaft of the block have different sizes. Due to this, the rotational moment of the engine is slightly extinguished, the crankshaft speed decreases, it receives a smaller load, and parts of the compression block wear less.
When choosing a specific compressor model, you should ask the seller what type of equipment it belongs to - domestic or professional. Household units are made of simple, inexpensive and sometimes not very high-quality materials, require interruptions. Professional devices are analogs of household compressors, but in their manufacture high-quality, wear-resistant parts are used. In addition, professional equipment can work without overheating for a long time.

/rating_off.png)










